Enteral
The term, enteral, refers to nutrition administered via the gastrointestinal tract. It may be administered orally or via tube feeding.
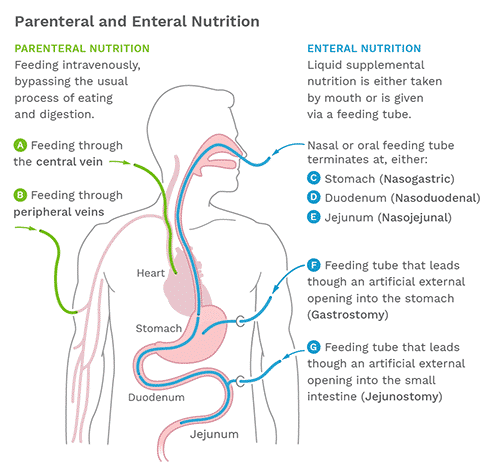
The term, enteral, refers to nutrition administered via the gastrointestinal tract. It may be administered orally or via tube feeding.
Oral nutritional supplements (ONS) are nutrition support products that provide an effective and non-invasive way for people to meet their nutrition needs or increase their nutritional intake. People who take ONS may also be able to eat regular food but cannot meet all their nutritional requirements through a regular diet alone and thus require supplemental nutrition. In other instances, a patient can benefit from ONS if they require a liquid-based diet. ONS products are often prescribed or recommended by a physician or registered dietitian. In some cases, people rely on ONS as their sole source of nutrition.
If a person has a condition or illness which limits or impairs oral intake, enteral nutrition (EN) therapy can be administered directly into the gastrointestinal tract as a tube feeding.¹ Enteral nutrition via tube feeding provides life-sustaining nutrients and is often required as a first option feeding method when a person is unable to consume food orally and/or has an impaired digestive system. EN therapy includes specialized liquid feedings containing protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients needed to live. These nutrition support products are formulated to meet individual needs for a variety of disease states and conditions.
Parenteral nutrition (PN) is the intravenous administration (feeding into a vein) of nutrients directly into the systemic circulation, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract.² It is a special liquid mixture containing protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients needed to live. PN represents an alternative or additional approach for nutrition intervention when nutrition needs cannot be met from the oral or enteral routes alone, or are contraindicated.